Search Results
Results for: 'fluorescent color'
SNP Polymorphysim Microarray Chip - How to Test a Person's DNA
By: HWC, Views: 5944
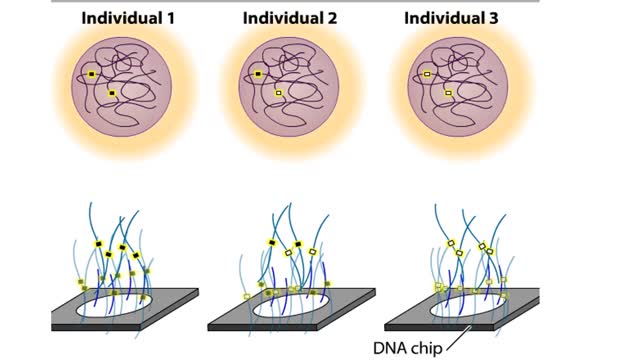
To test a person's DNA, a researcher first needs a source of tissue. Most of the cells in a blood sample are red blood cells, which lack nuclei, but there are also a number of white blood cells, which do contain nuclei and chromosomal DNA. If we could see a particular DNA sequence in these cel...
Sex-Linked Traits! How are eye colors inherited in fruit flies?
By: HWC, Views: 5735
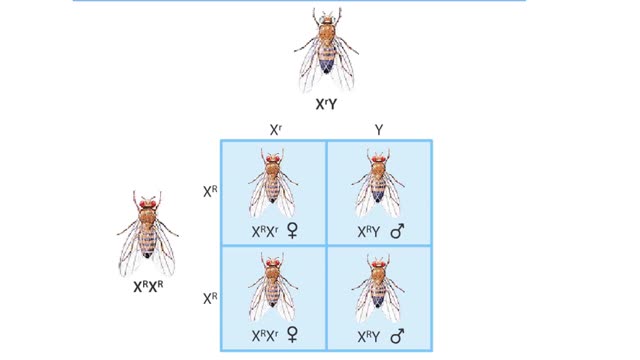
The eye color gene is located on the X chromosome (one of the sex determining chromosomes of Drosophila). White eye color is recessive. When a red eyed male mates with white eyed females, their daughters will have red eyes, but their sons will have white eyes.
By: HWC, Views: 4447
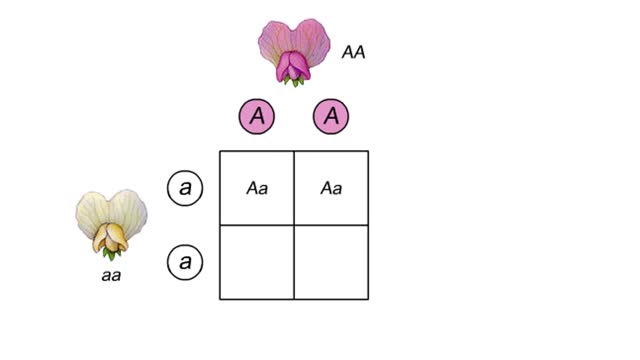
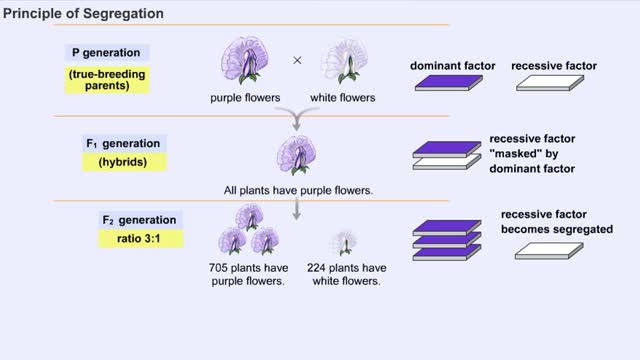
A monohybrid cross is a cross between two parents that breed true for different versions of a single trait. In this example, that trait is flower color. The allele that specifies purple flowers is dominant over the allele that specifies white flowers. The purple-flowered plant has two domin...
By: HWC, Views: 6054
Sugar snap peas were common garden plants during Mendel's lifetime and many varieties undoubtedly grew in the abbey gardens. An avid gardener. this is where Mendel first made observations about pea plants. He noticed that certain characteristics of peas were passed from generation to generation. ...
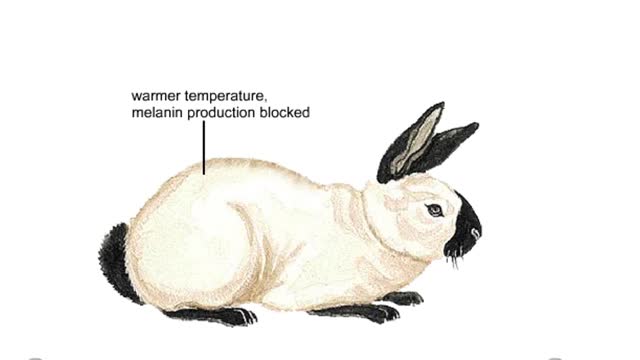
Effect of the environment on coat color in the Himalayan rabbit Animation
By: HWC, Views: 2234
An organism's phenotype—the combination of traits that we observe—is the product of interactions between its genotype and the environment. For example. a Himalayan rabbit is completely white at birth. But within weeks, the fur on the rabbits ears, nose, tail. and lower legs darkens. The...
Mendel's Principles of Dominance, Segregation and Independent Assortment
By: HWC, Views: 6156
Mendel selected true-breeding parents with contrasting traits, for example, purple and white flower color, and performed reciprocal crosses by choosing pollen from one parent and hand pollinating the seed-forming parent with this pollen. A cross-fertilization resulted from this procedure. In t...
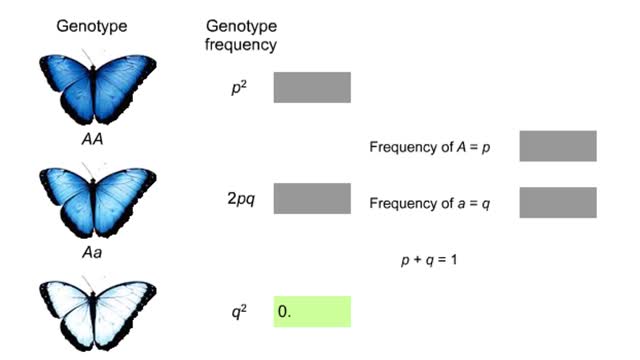
How to find out if a population is evolving?
By: HWC, Views: 3593
Imagine a butterfly population with a pair of alleles that influence wing color as shown. We will represent the frequency of the dominant allele as p and the recessive allele as q. The Hardy-Weinberg rule describes what happens if a population is at genetic equilibrium—if it is not evolving...
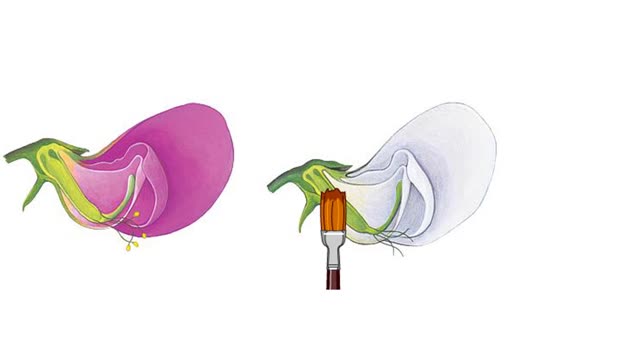
Mendel's pea plant, Pisum sativum experimental
By: HWC, Views: 4505
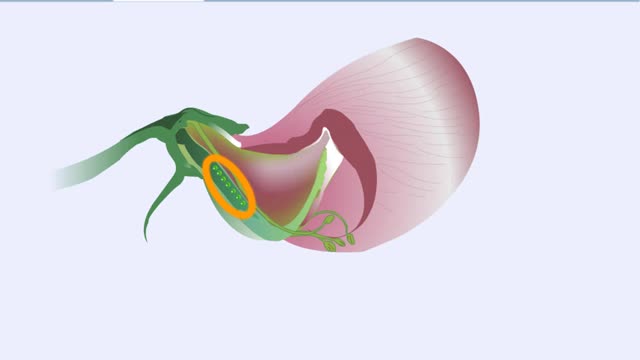
Mendel chose the garden pea plant, Pisum sativum, for experimental tests of his ideas about inheritance. Under normal circumstances, the garden pea plant is self-fertilizing. This cross-section shows the gamete-forming structures. Sperm-producing pollen grains form in the stamens. Eggs deve...
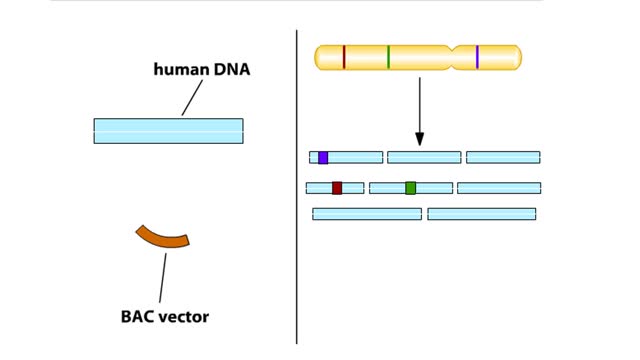
Hierarchical Sequencing Method - Sequence Tagged Sites
By: HWC, Views: 5860
In the hierarchical sequencing method, researchers begin by collecting cells. In humans, each cell contains 23 pairs of chromo-somes. Here we specifically track the DNA from just one of the 23 pairs. Chromosomes have a series of unique DNA sequences, called sequence-tagged sites (STSs), that a...
Advertisement